What Is Calorie?
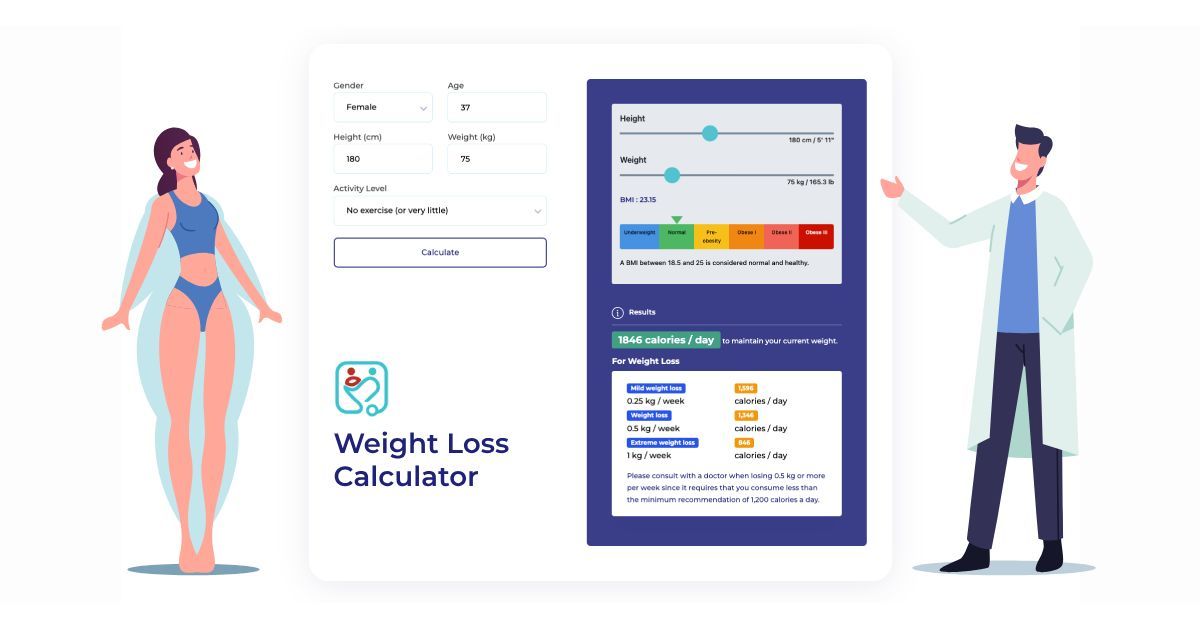
A calorie is a unit of energy. The term "calorie" is scientifically defined as the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. However, the calorie we talk about is the amount of energy in what we eat and drink, the calories in food provide energy in the form of heat so that our bodies can function even at rest. The total number of calories you burn each day is called your total daily energy expenditure. The calories you burn to maintain basic body functions like breathing and blood circulation.
Weight Loss Strategies
The principle of weight loss is simple: energy intake is smaller than energy expenditure. When you eat fewer calories than you burn, you create a weight loss, also known as “calorie deficit” or “energy deficit”. Calories burned through exercise and non-exercise movement; calories burned during digestion.
However, overweight and obesity are clearly the result of a complex set of interactions among genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors. The primary goal should be to foster an environment that promotes maintenance of a healthy body weight and body composition.
Increased physical activity is an essential component of a comprehensive weight loss strategy for overweight adults who are otherwise healthy. One of the best predictors of success in the long-term management of overweight and obesity is the ability to develop and sustain an exercise program.
While calorie intake is crucial, it's equally important to focus on nutrient-dense foods. By using our Calorie Weight Loss Calculator and following these tips, you can achieve your goals in a healthy and effective manner. Remember, sustainable weight loss takes time and patience, here are some tips to help you lose weight healthily:
- Eat frequently: consume smaller meals more often throughout the day to keep your metabolism active.
- Choose nutrient-dense foods: opt for foods rich in protein, fiber, and healthy fats, such as lean meats, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Limit processed foods and sugary drinks: these foods are often high in calories and low in nutrients.
- Stay hydrated: drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Incorporate regular exercise: aim for a combination of cardio and strength training exercises.
- Get enough sleep: adequate sleep is essential for weight management.
- Consult a healthcare professional: if you have underlying health conditions or concerns about your weight, consult with a doctor or registered dietitian. Be aware that any sudden and heavy weight change may cause harm to your health. Please consult with a doctor or registered nutritionist to plan your long-term nutrition and exercise program when your target is to lose 0.5 kg or more per week. Today, more than half of adults have one or more diet-related chronic diseases. Chronic patients should consider medical nutritional therapy in the overall planning and implementation of chronic disease management.
Souce: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK221839