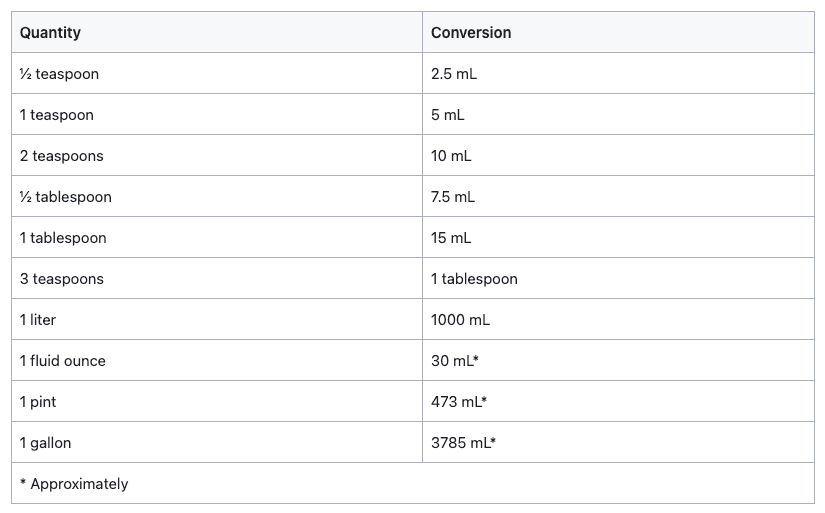
Liquid Measurement Conversions
How many mL in a teaspoon? How many fluid ounces in one liter? Trying to measure a liquid without a proper measure or converting information from the imperial to metric systems can be confusing.
Abbreviations
- Teaspoon = tsp
- Tablespoon = Tbsp or Tb
- Milliliter = mL
- Liter = L
- Fluid ounce = fl oz
- Pint = pt
- Gallon = gal
Note: Fluid ounces are a measure of volume while ounces are a measure of weight.
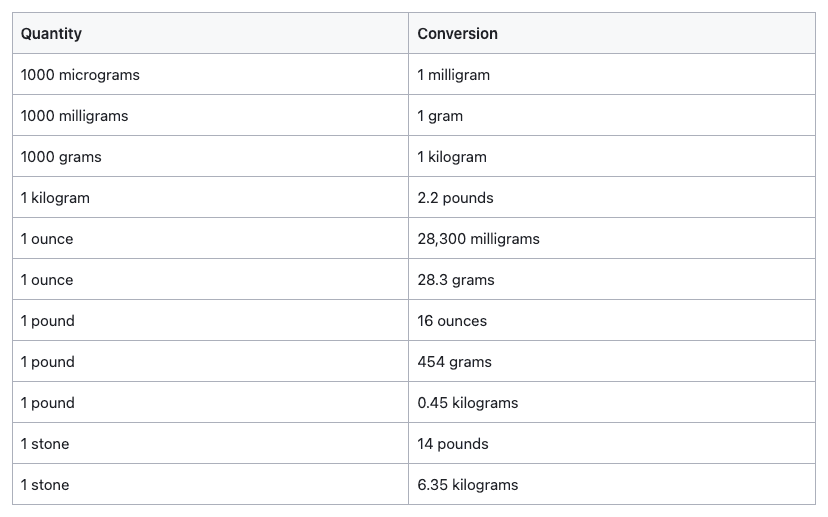
Solid Measurement Conversions
How many mcg in an mg? How many mg in an oz? Measurement conversions for solids can be confusing, particularly when many of the units sound the same.
Abbreviations
- Microgram = mcg (may also be written µgm)
- Milligram = mg
- Gram = gm
- Kilogram = kg
- Ounces = oz
- Pounds = lbs
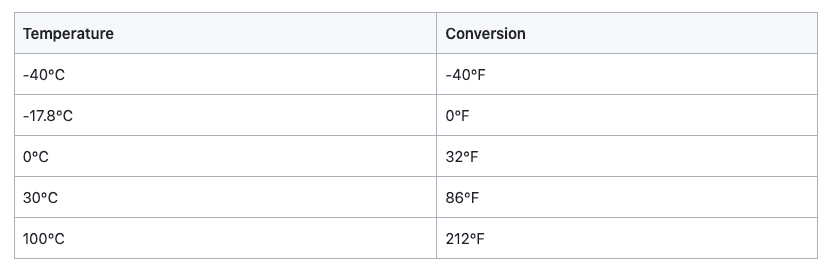
Temperature Measurement Conversions
To convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, take the Fahrenheit temperature and subtract 32, then multiply this number by 5, then divide the answer by 9 to obtain the temperature in degrees Celsius.
To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, take the Celsius temperature and multiply it by 1.8, then add 32 to obtain the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit.
The Celsius and Fahrenheit scales meet at -40°. Above -40°, Fahrenheit temperatures are always higher than corresponding Celsius temperatures, and below -40°, Fahrenheit temperatures are lower than the corresponding Celsius temperatures.
Abbreviations
- Celsius = C
- Fahrenheit = F
The Kelvin Temperature Scale
The Kelvin temperature scale is called an absolute temperature scale because it begins at zero and progresses in only one direction (there are no negative temperatures in the Kelvin scale).
The zero point of the Kelvin scale is absolute zero, which is the theoretical temperature at which molecules of a substance have their lowest kinetic energy and cannot get any colder. The Kelvin scale is defined using the third law of thermodynamics.
The Kelvin scale is related to the Celsius scale but is conventionally written without the degree symbol. Zero kelvin (written 0k) corresponds to −273.15°C on the Celsius temperature scale.
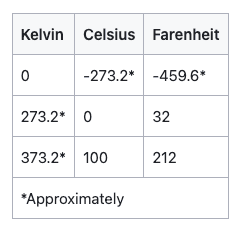
Note that 1 kelvin has the same magnitude as 1 degree Celsius, as seen by the difference between the freezing and boiling points of water of 100 degrees Celsius (or 100 kelvins).