Understanding Your Blood Sugar Test Results
A blood sugar test measures the amount of glucose in your blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that your body uses for energy. When you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into your bloodstream.
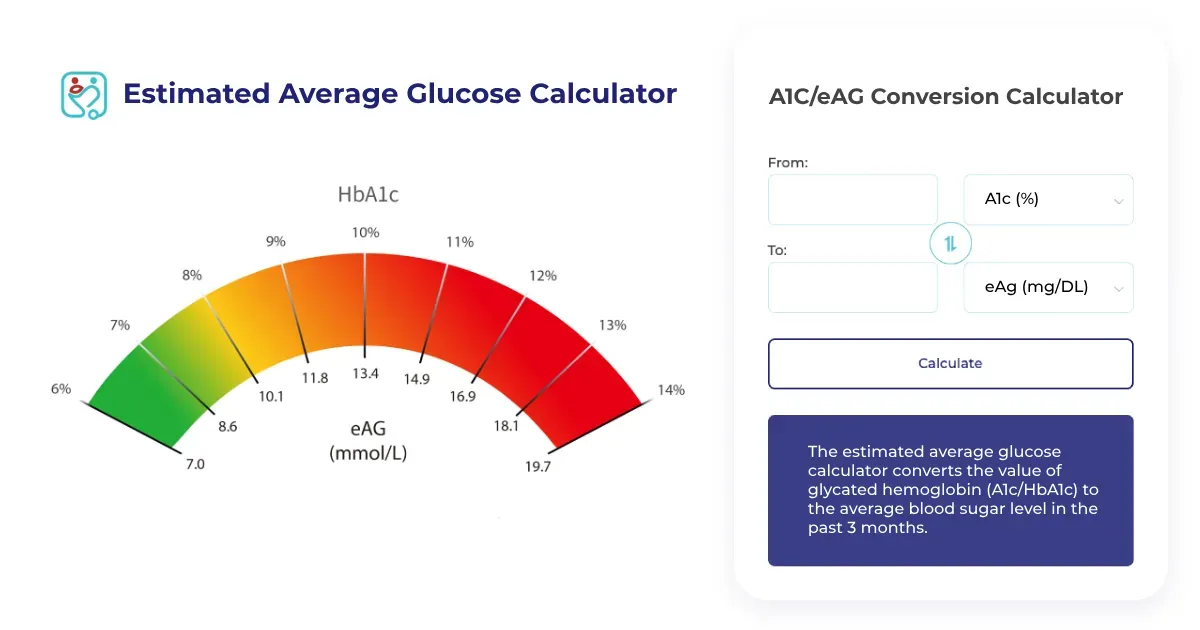
A1C, HbA1c Test
An A1C test, also known as a Hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) or glycated hemoglobin test, is a blood test for diabetes and prediabetes, that provides a picture of your average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months. This test measures the percentage of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, that has glucose attached to it. The higher the percentage, the higher your average blood sugar level has been.
A1C results are typically reported as a percentage. The following ranges are used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes:
- Normal A1C level is lower than 5.7% (eAG level is lower than 117 mg/dL)
- Prediabetes A1C level is between 5.7% and less than 6.5% (eAG level is between 117 mg/dL and less than 140 mg/dL)
- Diabetes A1C level is higher than 6.5% (eAG level is higher than 140 mg/dL)
Reference: https://diabetes.org/about-diabetes/a1c
Fasting Blood Sugar Test
Fasting Blood Sugar Test: a healthcare provider will prick your finger or use a needle to draw blood from a vein in your arm. Don’t eat or drink anything (except water) for 8 to 12 hours before the test. It's used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes. The following ranges are used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes:
- Normal (between 70-100 mg/dL or 3.9-5.6 mmol/L): normal fasting blood glucose concentration indicates you're at healthy blood sugar control.
- Prediabetes (between 100-125 mg/dL or 5.6-7.0 mmol/L): impaired fasting glucose concentration indicates you're at increased risk of developing diabetes.
- Diabetes (higher than 126 mg/dL or 7.0 mmol/L on two separate tests): you have diabetes.
Reference: https://www.who.int/data/gho/indicator-metadata-registry/imr-details/2380#:~:text=The%20expected%20values%20for%20normal,and%20monitoring%20glycemia%20are%20recommended.
Home Blood Sugar Test
Use a blood sugar meter (also called a glucometer) or a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) to check your blood sugar. A blood sugar meter (glucometer) measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip. A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) uses a sensor inserted under the skin to measure your blood sugar every few minutes. If you use a CGM, you'll still need to test daily with a glucometer. This will help make sure your CGM readings are accurate.
Random Blood Sugar Test: this test measures your blood sugar level at any point in time. The normal blood sugar result should be:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL.
- Two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
Reference: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/treatment/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/manage-blood-sugar.html